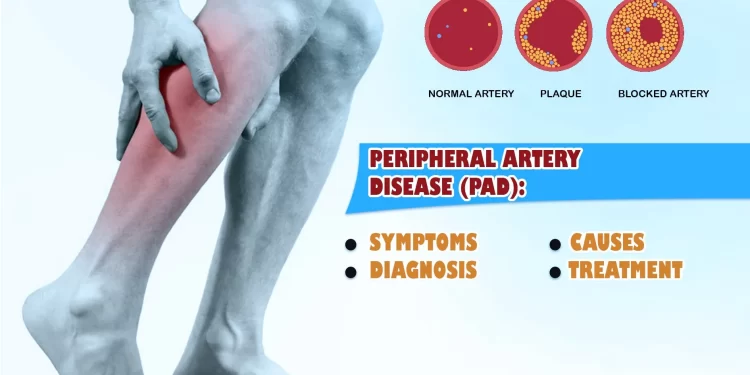
1. Introduction to Peripheral Artery Disease
It’s important to know what to do and where to get help when you notice any of these symptoms. This is where the work of a Vascular and Interventional Centre in Singapore comes into play. PAD is a major health burden in the older population. The local prevalence varies from 3-10%. Within the Asian region, the variation is also large. In a recent cross-sectional study, where patients with either coronary artery disease and/or cerebrovascular disease were compared, the prevalence of PAD in Singapore was shown to be 3.76% whereas in Japan it was 8.77%.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem. It occurs when arteries become narrowed or blocked by plaque – a condition known as atherosclerosis. For many, the symptoms of PAD can be mild or non-existent, leading to a lack of proper diagnosis and treatment. However, it’s important to take the condition seriously. If left untreated, PAD can progress and lead to severe limb and life-threatening health issues.
2. Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors
Some of the most common causes of peripheral artery disease are high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. Diabetes and obesity are other risk factors. As a person ages, the risk of developing peripheral artery disease increases, and it is most common in people over 65 years of age. Men are more likely to get the disease than women. Also, the American Heart Association estimates that about 8.5 million people in the United States have PAD. However, because many people may have the disease and not show any symptoms, it’s difficult to pinpoint the exact number. For those who do show symptoms, the pain and discomfort that comes with the disease can become debilitating. Left untreated, severe cases of peripheral artery disease may result in tissue death and can sometimes lead to gangrene, or the death of the tissue, primarily from a loss of blood supply.
3. Recognizing the Symptoms and Diagnosis
Another key point discussed in the article on PAD is that of recognizing the symptoms related to the disease. Many people with this disease may be asymptomatic and therefore awareness of its potential signs is crucial. Symptoms such as pain and cramping, particularly in any part of the leg, thigh or buttock, when the patient is walking that disappears when the patient stops – known as intermittent claudication; or the development of non-healing wounds on the feet or toes are all signs that a patient may have PAD. It is important to seek help from healthcare professionals which may involve doing a physical examination, ankle-brachial index test and so on in order to identify the existence and severity of PAD in a patient because a patient with PAD has a higher risk of coronary artery disease, where it may cause a heart attack or stroke. Those with the disease should seek help from Vascular and Interventional Centre, a specific type of medical service that offers minimally invasive treatment for vascular conditions – in Singapore in order to get professional assistance.
4. Treatment Options for Peripheral Artery Disease
There are several ways to treat peripheral artery disease. Making lifestyle changes and getting regular exercise can help improve the symptoms of PAD. However, if PAD has progressed, a medical or surgical intervention is often needed. Medication is a common treatment option for PAD. These can help to lower cholesterol levels, control high blood pressure and manage the symptoms of the disease. There are also medications which can help to improve the circulation of blood in the body, such as cilostazol and pentoxifylline. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe antiplatelet drugs, which help to reduce the likelihood of blood clots forming. If the symptoms of PAD are severe, a doctor may recommend a minimally invasive treatment called angioplasty. This involves inserting a special type of balloon into the arteries of the legs which is then inflated in order to widen the arteries and restore blood flow. A small metal tube known as a stent may be inserted during the procedure. This helps to provide support to the artery walls and reduces the likelihood of the artery narrowing again in the future. For some patients with PAD, bypass surgery may be the best treatment option. This involves redirecting the flow of blood around a section of the artery which has become narrowed or blocked. In order to redirect the flow, the surgeon will use a blood vessel sourced from another part of the body to create a detour. This could be a vein taken from the patient’s leg or an artificial blood vessel.
5. Seeking Help from Vascular and Interventional Centre in Singapore
You can seek help from Vascular and Interventional Centre in Singapore if you are diagnosed or suspected to have peripheral artery disease. A vascular doctor, also known as a vascular or endovascular specialist, is a doctor who is trained to treat blood vessel conditions. He will review your medical history and symptoms, conduct a physical examination like measuring blood pressure at various levels of your leg arteries, and arrange for imaging tests like ultrasound, CT, or MRI to evaluate the blood flow and the condition of your blood vessels. After evaluation, your vascular doctor will discuss the test results and explain the diagnosis. He will also work with you on your treatment plan. Treatment options for peripheral artery disease include making lifestyle changes, taking medication to control the risk factors, and undergoing procedures to improve blood flow in the affected legs. You can be assured of quality treatment if you seek treatment from a vascular and interventional center in Singapore where the center provides a comprehensive range of services, from diagnosis to treat various vascular conditions. The center is equipped with the latest technology and infrastructure for a speedy, accurate, and comprehensive diagnosis and treatment for various arterial and venous conditions. Most importantly, the center has a dedicated team of vascular and interventional radiologists who specialize in minimally invasive, targeted treatment using imaging guidance, which includes the newer and established procedures. These minimally invasive methods can often provide an alternative to traditional surgery with less risk and shorter recovery time. Lastly, the vascular and interventional center in Singapore is supported by a team of healthcare professionals, including specialist nurses, therapists, and technologists who have expertise in vascular health. From intervention planning, treatment to aftercare, each and every patient will be well taken care of to ensure the effectiveness and success of the treatments, and also to promote a good and sustained recovery. Seeking help and treatment from a vascular and interventional center in Singapore is therefore definitely a great choice for effective and comprehensive management of vascular conditions like peripheral artery disease.